Arthosis is a disease characterized by the gradual destruction of the joint due to the development of dystrophic changes in the tissues.According to those who, every tenth resident of the planet is faced with this problem.After 50 years, the risk of the onset of the disease is about 30%and 70 years old reaches 80-90%.
General information
Arthosis is a long -term chronic process that affects not only the joints.As it advances, the dystrophic and degenerative changes are also surprising the auxiliary apparatus.In the process, the patient is faced with the inflammation of the cartilage and bone tissue, the joint capsule and the periosemic bag, as well as the muscles, ligaments and subcutaneous tissue that contact them.
Regardless of the location, the pathological process passes according to a single scheme.Firstly, in the thickness of the fabric, the balance between the growth processes and the destruction of the cartilage is disturbed and the balance is moved in favor of dystrophy and reverse development (degeneration).At this moment, invisible changes to the eye in the microstructure of cartilage occur, which leads to its thinning and cracking.
As the disease advances, the joint loses its elasticity and becomes more dense.This reduces its ability to depreciate, the rate of damage to the fabric is constantly increasing due to vibrations and microtrauma during movements.The thinning of the cartilage layer causes the active growth of bone structures, following which peaks and protrusions develop on the smooth surface of joint osteoarthritis.Movements become increasingly limited and painful.Spasms of muscles surround the affected area, which aggravates pain and deforms the limb.
Disease phase
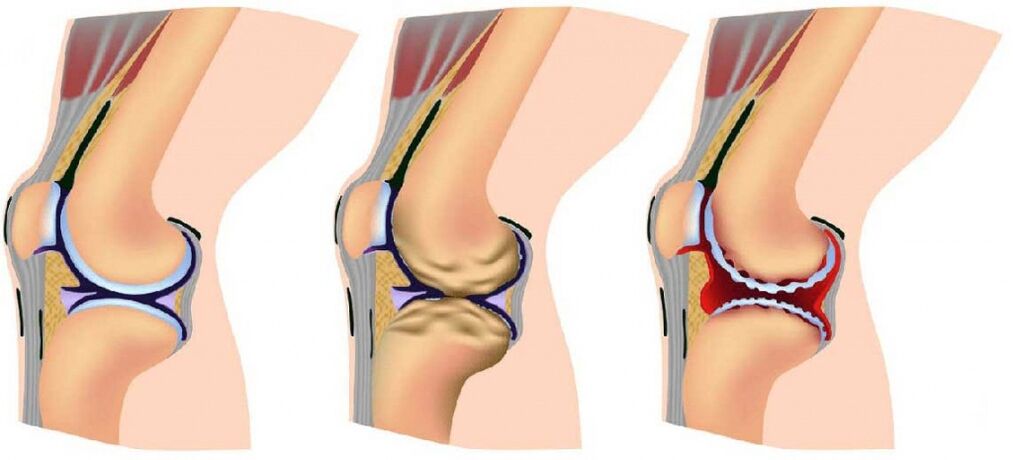
The arthrosis of the joints develops gradually and in the process three sequential stadiums that determine the severity of the disease:
- Phase 1: the pathology is not detected on an X or ultrasound radius, but the processes of destruction have already been launched;The composition of the joint fluid changes, following which the tissues are obtained less than nutritious creatures and become more sensitive;The increase in the load on the damage area causes inflammation (arthritis) and pain;
- The second phase is characterized by the active destruction of the cartilage tissue and the peaks and bone growths appear along the edges of the joint platform (area of contact of the surfaces);At this moment, the pain becomes familiar and the inflammatory processes become stronger or weaker;The spasms associated with the muscles joint are periodically noted;
- Phase 3: the areas of destruction affect almost the entire surface of the cartilage, the joint platform is deformed, the injured limb differs from its axis;The volume of the movements is reduced and the ligaments weaken and are short.
Some experts also distinguish the IV stadium of the development of arthrosis.It is characterized by the almost complete immobility of the joint.
Types
Depending on the cause of the disease, primary and secondary arthrosis are distinguished.In the first case, the pathology arises independently of the background of a complete effect of the predisposing factors.The secondary form is the result of other diseases and is divided into the following groups:
- damage to the joints that occurred due to metabolic disorders or endocrine diseases (gout, diabetes mellitus, acromegaly, hyperparathyroidism);
- Destruction associated with congenital pathologies (pedgetic disease, congenital dislocation for lips, scoliosis, hemophilia, etc.);
- The arthrosis post -traumatic, which occurred against the background of fractures, cracks, necrotic processes or surgical operations, as well as due to the characteristics of the profession.
The most requested is the classification of osteoarthritis, depending on the location of the pathological process:
- Gonartrosi: the knee injury, one of the variety of which is the arthrosis Pace -palet - the destruction of the articulation between the femoral bone and the patella;
- Arthrosis of the ankle joint: it occurs against the background of a large load and frequent injuries;
- Arthrosis of the joints of the foot: the thumb often suffers from the junction with the foot;The defeat develops against the background of the gout or valgus deformation;
- The arthrosis of the shoulder is characterized by shoulder damage and is often located at a young age on a background of greater physical activity (engines, athletes, manufacturers);
- Coksartrosis: damage to the hip joint;Perhaps it is one side and bilateral and is one of the frequent causes of disability in people over 50;
- Vertebral arthrosis: the destruction of cartilaginous discs between the vertebrae, the most often affects the cervical and lumbar column;
- Articles of the brush joints: the joints of the fingers are often affected, pathologies are particularly susceptible to menopause women;
- Arthos of the Temporo -Mandibular joint: it is rather rare, very often against the background of chronic inflammation due to bite disorders or improper prostheses;
- Arthos of the elbow joint: a rare form of illness, very often associated with injuries in this area.
The reasons for development
The main factor in the development of arthrosis is the lack of correspondence between the test and the joint ability of the joint to resist this load.Acute or chronic, this process inevitably leads to the destruction of the tissues.
The list of causes that increase the risk of arthrosis of any location includes:
- inheritance;
- Endocrine pathology (diabetes);
- Lessions of the joint apparatus: bruises, dislocations, fractures or crepe of bones within the joint bag, full or partial pauses of ligaments that penetrate the wounds;
- joint load increased regular associated with the profession;
- obesity;
- hypothermia;
- Transferent inflammatory diseases: acute arthritis, tuberculosis, etc.;
- Blood diseases in which hemorrhages often occur in the joint (hemophilia);
- important changes in the hormonal background (pregnancy, menopause);
- local circulatory disorders in relation to atherosclerosis, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, etc.;
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.);
- Dyplasia of the connective tissue (congenital pathology, accompanied, including the excessive mobility of the joints);
- congenital pathologies of the musculoskeletal system (plates, dysplasia or congenital dislocation of the hip joint, etc.);
- age over 45-50 years (the increase in risk is associated with a decrease in collagen synthesis);
- osteoporosis (bone empty);
- chronic body intoxication (including salts of heavy metals, drugs, alcohol);
- Surgery on the joints.
Symptoms
The symptoms of arthrosis practically independent of its cause and location, since changes in the joints go according to the same scenario.The disease gradually develops and begins to manifest itself, already when the cartilage is quite seriously damaged.
One of the first signs of dysfunction is the creaking in the area of the problem during the movement.Very often, it occurs when the knee or shoulder are damaged.At the same time, a person can try a slight decrease in mobility after prolonged inaction, for example, in the morning.
When asked what symptoms they appeared with arthrosis, most patients call first pain.Initially, insignificant and weak, he gradually earns strength, preventing himself normally.Depending on the stage and location of the pathology, a person may feel:
- Initial pains: they occur during the first movements after the prolonged inaction of the joint and are associated with the formation on the surface of the cartilage of the thin film with the destroyed tissue;After the start of the work, the film moves and the discomfort disappears;
- Pain with prolonged physical effort (standing, walking, running, etc.): it appears due to a decrease in shock properties -absorption of the joint;
- Meteorological pain: caused by low temperatures, humidity, variations in atmospheric pressure;
- Night pain: associated with venous stagnation and increased blood pressure within the bones;
- Joint block: acute and severe pain associated with the violation of a piece of cartilage or bone located in the joint cavity.
As arthrosis develops, the symptoms become more evident, the patient detects the following signs:
- an increase in morning rigidity;
- strengthen and increase the duration of pain;
- decrease in mobility;
- joint deformation due to bone growths;
- Deformation of the bones and the surrounding fabrics: the process is clearly evident on the limbs and fingers of the hands, which become considerably curved.
When inflammation is attacked, the affected area swells, blushes and becomes warm to the touch.Press on it causes a strong increase in pain.

Analysis and diagnostic
The diagnostics of arthrosis is engaged in the orthopedic doctor.He leads a detailed patient investigation to identify complaints and anamnesis.The doctor in detail on the time of the appearance of the first signs and the speed of their development, injuries and diseases, the presence of similar problems in relatives.
A general blood test allows you to identify an inflammatory process, which often accompanies arthrosis.
The main method of diagnosis is radiography.In the photo, the following signs are clearly displayed:
- narrowing of the joint gap;
- Change the contours of the contact bones;
- bone structure disturbed in the area concerned;
- Bone growths (osteophytes);
- curvature of the axis of the limb or finger;
- Subluxation of the joint.
For more detailed diagnostics, they can be prescribed:
- computerized tomography (CT);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Ultrasound of the joint;
- arthroscopy (internal examination of the joint cavity using a camera introduced through a small drilling);
- Scintigraphy (evaluation of the state of the bones and the metabolism in them for the introduction of radiopharmaceutical drugs).
In case of suspicion of the secondary nature of the disease, appropriate tests and consultations of restricted specialists are prescribed.
Treatment of arthrosis of the joints
The choice of the methodology for the treatment of arthrosis of the joints depends on the cause of the disease, its stages and symptoms.In the arsenal of the doctors there are:
- drugs;
- non -drug treatment;
- Surgical methods.
In addition, the patient must strictly observe a diet and adjust his lifestyle in order to minimize further damage to the joints.
Pharmacological treatment
The appointment of arthrosis drugs pursues two main objectives:
- removal of pain and inflammation;
- Restoration of the cartilage tissue or, at least, further stop degeneration.
To facilitate the patient's condition, various types of drugs are used:
- Regulations anti -ninflammatory non -pounds in the form of tablets, injections, ointments or candles;They relieve pain and inflammation well;
- Hormones (corticosteroids): shown in severe pain and, very often, they are introduced directly into the joint cavity;
- Other analgesics, for example, antispasmodic action: helping to reduce the level of pain by relaxing the muscles;
It is important to remember: all types of painkillers are used only to facilitate the patient's condition.They do not influence the conditions of the cartilage and with prolonged use they accelerate its destruction and cause serious side effects.
The main preparations for the restoration of the joints today are the chondroprotectors.They contribute to the saturation of the cartilage with nutrients, stop the monument and begin cell growth processes.The means have an effect only in the initial and medium phase of the development of the disease and subject to long -term regular use.
Preparations that improve microcirculation in anti -mezzi fabrics and content help improve the effect of chondroprotectors.The first provides a good supply of the area concerned with oxygen and nutrients and the second slows down the processes of destruction of the tissues.
The selection of specific drugs, their dosage and the administrative regime are engaged in the doctor.
Non -drug treatment
Non -pharmacological treatment includes the following methods:
- physiotherapy:
- Brunette therapy: it destroys bone growth and stimulates blood circulation due to the effects of ultrasound;
- Automated electromystimulation: exposure to electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contraction;
- UltraPhonophoresis: the effect of ultrasound in combination using drugs;
- Ozonotherapy: the introduction of a special mix of gas in the joint capsule;
- physical education of physiotherapy;
- Mechanics: operating therapy with simulators;
- Joint traffic to reduce the load;
- massage.
Surgical treatment
Very often, the help of a surgeon is required in the serious stages of the disease.Depending on the location of the pathological process and the degree of injury, it can be prescribed:
- Punting: a drilling of the joint with the removal of a part of the fluid and, according to the indications, the administration of drugs;
- Corrective osteotomy: removal of the bone part, followed by the fixation from a different angle to remove the load from the joint;
- Endoprostetica: replacement of the damaged joint with a prosthesis;Used in extremely neglected cases.
Arthrosis in children
Arthosis is considered a disease of the elderly, but can also be found in children.The most common cause of the pathology is:
- congenital pathology of the connective tissue;
- serious injuries;
- inheritance;
- Metabolic disorders and the work of the glands of internal secretion;
- orthopedic disorders (flat feet, scoliosis, etc.);
- overweight.
The arthrosis of children is rarely accompanied by pronounced symptoms: the pain is painful and practically there is no rigidity and limitation of the function.The monothetic changes are detected on an X ray, magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound.In the processing process, the same products are used in adults.The utmost attention is paid to exercise and physiotherapy therapy, since they are particularly effective at a young age.Without treatment, the disease sooner or later passes into the advanced phase with a complete loss of mobility.
Diet
Diet is one of the most important factors in the treatment of osteoarthritis.In the presence of excess weight, it is necessary to reduce it to reduce the load on the joints.In this case, a balanced diet is prescribed with a deficiency of calories.Regardless of the body mass index, doctors recommend that they completely abandon:
- fast carbohydrates (sugar, dessert, flour);
- alcohol;
- spices;
- legumes;
- strong tea and coffee;
- Excessively fat and sharp dishes.
In box and offal they are not excluded, but significantly limited, as well as salt.The ideal nutrition for osteoarthritis includes:
- lowly meat fat varieties;
- fish and seafood;
- egg;
- Lactiero -Caseari products;
- flax and olive seed vegetable oils;
- vegetables and fruit, a large amount of vegetables;
- Moderate cereals, hard pasta -Wrap pasta;
- Products with a high collagen content (gelatin, payment, gelatin).
Prevention
Arthosis is easier to warn than to be treated.To maintain joint health for many years, it is recommended:
- guide an active lifestyle;
- Exercise and visit the swimming pool regularly;
- Eat correctly, use quite Omega-3 and collagen;
- prevent the IMC overcoming;
- Wear comfortable shoes.
If the disease is diagnosed in an initial phase, it is recommended to regularly undergo the treatment of the SPA, as well as excluding professional risk factors: long -term residence on the legs, raising gravity, vibration.
Consequences and complications
Arthosis progresses very slowly.When performing the prescription of a doctor, its current slows down significantly, which allows you to maintain joint mobility much longer.The non -reversible consequences develop without treatment:
- Pronounced joint deformation;
- decrease in mobility until its complete loss (ankylosis);
- shortening of the limb (with knee damage or the femoral joint);
- Deformation of the bones, curvature of the limbs and fingers.
Forecast
The prognosis for arthrosis depends on the shape of the disease, the degree and the quality of the treatment.The pathology is one of the frequent causes of disability and, in advanced cases, the ability to move and self -service.In serious forms of damage to the joints of the knee and hip, the patient receives the first or second group of disabilities (depending on the stadium and the volume of damage).